Does Potting Soil Go Bad? Here’s How to Tell
Potting soil also known as potting mix is made from a mixture of organic and inorganic materials which provides nutrients and proper drainage that plants need to grow. When choosing potting soil, it’s important to consider its shell life, what your plants need and the ingredients used.
Using contaminated or expired potting soil can severely harm your gardening project. Bad soil can cause various problems for your plants including wilting, stunted growth, and yellowing leaves. So, this brings us to a question, does poting soil go bad?
Yes, potting soil can go bad over time or when inappropriately stored. The soil in unopened bags can last for up to 2 years when stored in a cool, dry place. Opened bags of potting soil will last for about 6 months or less when stored in a damp, hot, or contaminated place.
Peat moss is the main ingredient in most potting soils. It is a lightweight organic material that helps to retain moisture in the soil but over time, it decomposes and gets compacted. This is why most producers of potting soils are using coco coir instead of peat moss.

Does potting soil go bad
Apart from the composition factor, the shell life of your potting soil typically depends on how you store it. Potting soil should be tightly sealed in a bag and kept in a cool dry place. This not only prevents the moisture from escaping but also keeps it out of rich contaminants.
There are a number of things that can make the soil go bad. They include moisture, heat, pests, and chemical contaminants.
Moisture
Exposing potting soil to excess moisture before using it can cause it to go bad. Moisture speeds up the decomposition of peat moss and other organic materials in the soil. Moisture can also create a breeding ground for mold and mildew. These fungi can make the plants unhealthy.
To prevent moisture from contaminating your soil, it’s important to keep the bag sealed and well-kept in a cool dry place.
Pests
Soil can also be infested by dangerous plant pests when not properly stored. Mealybugs, thrips, fungus gnats, and spider mites can sneak into the soil especially when the bag is not properly sealed. Pests can harm the plants as soon as they are grown in the soil.
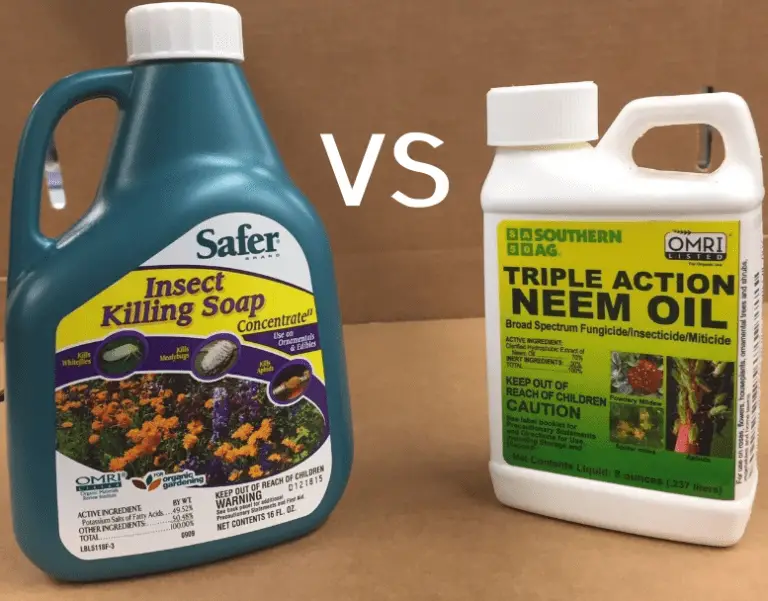
There is a need to sterilize potting soil if you suspect pests. Heating the soil in an oven or microwave to a temperature of 180 degrees Fahrenheit will kill all the pathogens and dangerous pests. You can treat the soil with a pesticide, but be sure to follow the directions on the product label carefully.
Heat
Heat can cause the soil to dry out quickly, and this can make it difficult for plants to take up water and nutrients. Additionally, heat can speed up the decomposition of peat moss, which can make potting soil go bad more quickly. Overheating the soil may also kill beneficial microbes.
Chemicals
Poor packaging or storage may expose soil to chemical contaminants. Storing potting soil with herbicides, pesticides, or VOC-containing products can make it unsuitable for gardening. Change in color and strong odor can be a sign of chemical contamination.
How to tell if your potting soil is bad
If you have stored your potting soil inappropriately for more than 6 months, here is how to tell if it’s still good or has gone bad.
- Check the color of the soil. Healthy potting soil is usually dark brown or black in color. If the soil is light or gray, it may be a sign of mold or mildew.
- Feel the texture of the soil. Healthy soil should be crumbly and easy to work with. If the soil is hard or compacted, it may be a sign of expiry.
- Smell the soil. Healthy soil should have a slightly earthy smell. If your potting soil has a strong, unpleasant odor, it may be contaminated with chemical compounds.
- Poor plant health. You may also tell that your soil is contaminated if it causes problems for your plants including wilting, stunted growth, and yellowing.
- Poor drainage. Potting mix without good drainage is a sign of bad soil.
If you suspect that your soil has a problem after planting, I recommend that you repot your plants in fresh potting soil. Check if your plants have any other problems including root rot and fix them as needed. Cut off any dead roots before repotting the plant.
What to do with old potting soil
If you cannot reuse your old potting soil, there are a few things you can do with it instead of disposing of it.
- Compost the old potting soil to improve the quality of your compost. Be sure to remove any debris, such as plant roots or rocks, and sterilize it before composting.
- Donate the soil to a local nursery or garden center. Some nurseries and garden centers will accept and recycle the old potting soil for the benefit of local the local community.
- Dispose of it properly. If you cannot compost, reuse, or donate your old potting soil, you will need to dispose of it properly. You can take it to a landfill or a designated hazardous waste disposal facility. Be sure to follow your local authority regulations for disposing of old potting soil.
Final Thought
Potting soil can last for two or more years when packaged and stored properly. Mishandling in the soil can result in contaminations that can harm your plants. If you suspect that your soil has gone bad, don’t use it for growing plants. Instead, sterilize and compost it or dispose of it in a landfill.
References
Common soil Problems – University of Maryland Extension
Soil Quality Information – Pennstate Extension
Soil and Plant Nutrition – University of Maine Extension
USDA. “Soil Quality Concepts.”
My name is Diane M Lewik, and I am the founder of this website. I am a degree holder in plant biology from the University of California – Berkeley. Over the years, I have cultivated a vast collection of succulents and I have learned a great deal about how to grow and care for these unique plants. Feel free to ask any questions in the comment section below.